Voice Biometrics uses a person’s unique voiceprint to identify authorized legitimate users. The solution offers an efficient and effective mechanism for “contactless” ID verification. With voice biometrics, remembering numerous passwords, waiting for OTPs, and toggling between multiple devices can become a relic of the past.
Many service providers offer Voice Biometrics solutions in two variants – Active and Passive Modes. In our previous article, we’ve seen how voice biometrics is revolutionizing call centers. The goal of this article is to learn about the methodologies and help you pick the best voice biometric method for your customers.
Active Voice Biometrics
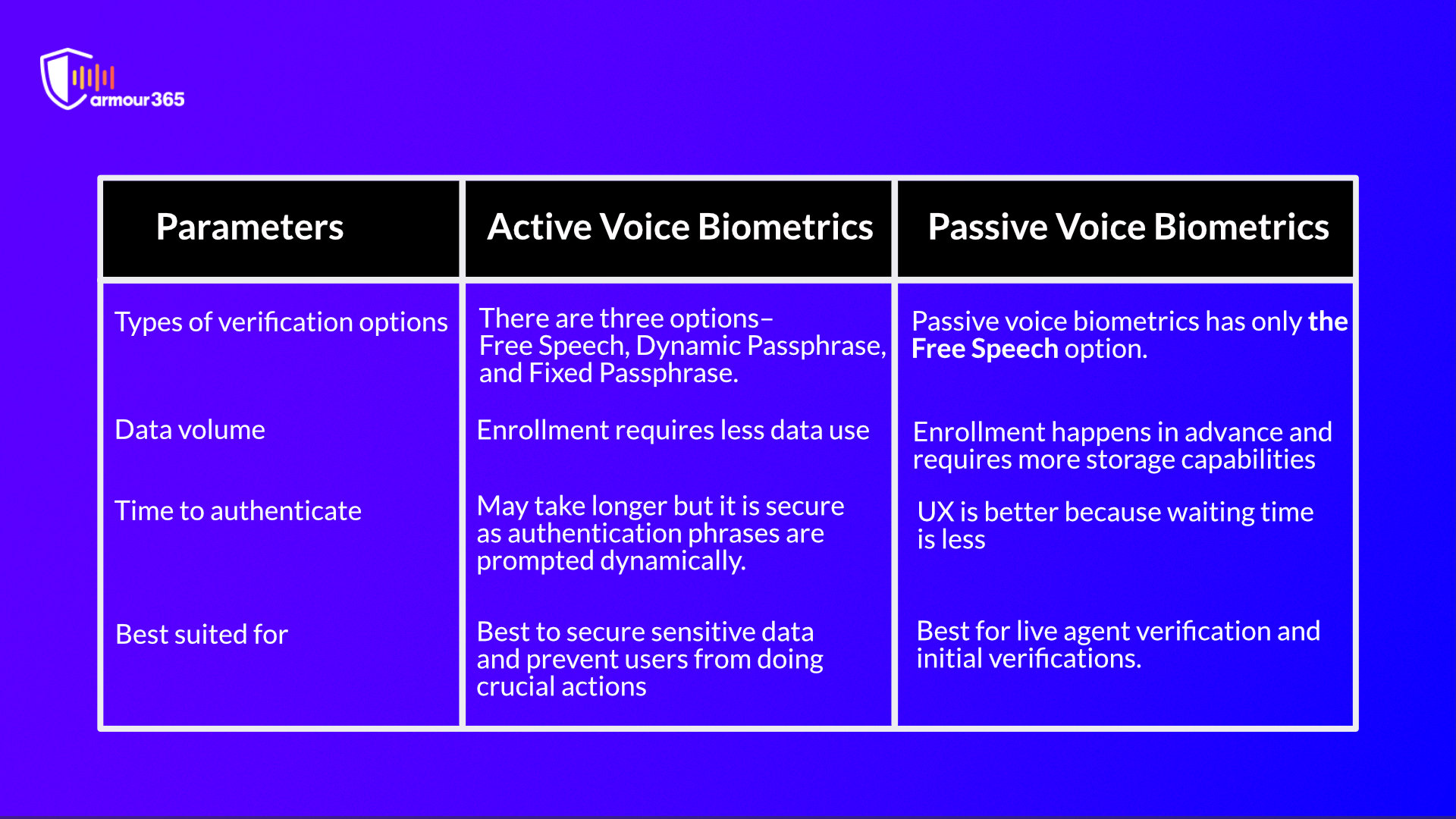
In the active voice biometrics, authentication is based on the utterance of a system-prompted passphrase or a guided natural speech. Under this method, active verification has three options-
Free Speech – The user is free to speak anything in multiple languages.
Dynamic Passphrase –The user is prompted to repeat a “one-time” generated passphrase, acting as a liveness check.
Fixed Passphrase – The user is asked to speak a “pre-set” passphrase, which ensures the user’s two-factor authentication.
Passive Voice Biometrics
Passive verification has only the free speech option. The user has to speak for a predetermined duration in passive verification or passive voice authentication, but this can happen organically.
As the verification happens automatically in the background, the user must not say anything specific like a passphrase or repeat anything multiple times. The system captures the user’s voiceprint in the background and tries to find the match as the user speaks.
Difference Between Active and Passive Voice Biometrics
The major difference between the two types of authentication, besides the methodology, lies in the customer experience.
After the enrollment, passive biometrics happens a lot faster when compared to active voice biometrics authentication because the verification happens automatically in the background as the caller converses normally with the bot or agent.
Generally, the user experience is directly proportional to the waiting time; the lesser the waiting time and the fewer questions required for the authentication, the better the customer experience will be. But, data security is also crucial in some cases. For example, patient health records are protected with the utmost care by healthcare institutions.
Therefore, passive voice authentication may be a good idea for general or initial interactions, and active voice authentication will be a good choice for conducting crucial actions & accessing sensitive data.
The enrollment process and time also differ a little. Active identity verification uses less data when enrolling users since they have to actively recite the passphrase. Whereas in passive verification, the voiceprints have to be collected beforehand. It also uses up more of the network’s computing and processing power.
However, being a mathematical pattern, the passive voiceprint is harder to replicate. Fraudsters attempt to hack by recording passphrases, so the active systems should be equipped with anti-spoofing layers. A detailed comparison of active vs passive voice biometrics is given in the table below for easier understanding.
Active Or Passive, Which One Is Best?
Both active and passive voice biometric authentication systems can be useful, but it depends on the organization’s needs. Therefore, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23.6% from 2021-2026.
A simple CX is a priority for some brands, and callers want high efficiency and low wait times. Passive voice authentication is a better choice if the same users don’t need to be authenticated for simpler queries and places where customers want their queries to be quickly attended. Interaction with live agents works better with passive voice biometrics.
Active voice authentication is a better choice for safeguarding healthcare and financial services that require a high degree of security and compliance.
Experiencing is always better than reading. Try our IVR demo to experience how voice biometrics works and make remote authentication easier.